In the world of plumbing and piping, flanges and fittings may not steal the spotlight, but they play an important role in connecting pipes, valves, and equipment, ensuring that fluids flow smoothly. Let’s explore these components, their types, materials, standards, applications, and emerging trends.
Understanding the Basics
Image source:Texas Flange
Flanges are flat discs with holes in the center, connecting various parts of fluid systems. Fittings come in different shapes and sizes and help redirect and modify fluid flow. Together, they are the backbone of fluid systems, making sure everything works as it should.
Material Matters
Flanges and fittings are made from different materials, chosen based on factors like fluid compatibility and strength. Common materials include steel, stainless steel, brass, and special alloys like Inconel for challenging conditions.
Types You Should Know
Image source:Texas Flange
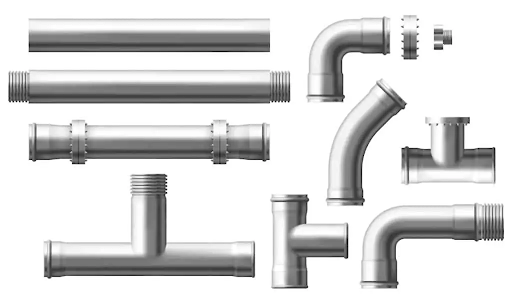
There are various types of flanges and fittings, each serving specific purposes:
Slip-on: Slides onto pipes for a secure fit.
Weld Neck: Welded to pipes for high-pressure applications.
Blind: Seals off flow with bolts.
Lap Joint: Designed for easy dismantling.
Threaded: For pipes with external threads.
Socket-weld: Provides a smooth bore for fluid flow.
Standards and Specifications
Flanges and fittings adhere to industry standards like ANSI/ASME, DIN, JIS, and ISO. Choosing the right standard is crucial for compatibility and safety.
Pressure and Temperature Considerations
Manufacturers make flanges and fittings to handle specific pressure and temperature demands, ensuring safe and reliable operation.
Image source:Texas Flange
Applications in Diverse Industries
Flanges and fittings are versatile and used in various industries:
Oil and Gas: Connecting valves, pumps, and vessels.
Chemical: Essential in heat exchangers and heating systems.
Water Supply: Backbone of industrial waterworks.
HVAC: Support efficient plumbing and mechanical systems.
Construction: Used in mining and fire protection systems.
Power Generation: Play a role in nuclear power systems.
Food Processing: Vital in valves, pumps, and vessels.
Future Trends and Innovations
The world of flanges and fittings is evolving:
3D Printing: Offers customization and faster production.
Smart Monitoring: Provides real-time data on system performance.
Sustainable Materials: Eco-friendly materials support sustainability.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions):
- What are flanges and fittings, and how do they work?
Flanges are flat discs with holes used to connect pipes, valves, and equipment in fluid systems. Fittings come in various shapes and sizes to redirect and modify fluid flow. They work by creating secure connections and ensuring fluid flows smoothly within a system.
- When should I use specific types of flanges and fittings?
Use slip-on flanges for secure fits, weld neck flanges for high-pressure applications, blind flanges to seal off flow, lap joint flanges for easy dismantling, threaded flanges for externally threaded pipes, and socket-weld flanges for smooth fluid flow.
- How do I choose the right material for my application?
Select materials based on factors like fluid compatibility, temperature, and corrosion resistance. Common materials include steel for durability, stainless steel for corrosion resistance, and brass for low-pressure systems.
- What standards should I consider when selecting flanges and fittings?
Consider standards like ANSI/ASME, DIN, JIS, and ISO to ensure compatibility and safety with your specific project requirements.
- Can I use flanges and fittings in high-temperature or corrosive environments?
Yes, you can by choosing materials that resist corrosion, such as stainless steel or specialized alloys like Inconel, and by ensuring the components meet the required pressure and temperature ratings.
- What advantages do flanges and fittings offer over other connection methods?
Flanges and fittings provide secure connections, easy assembly and disassembly, structural support, and adaptability to various system requirements. They are ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
- How do I maintain flanges and fittings for long-term reliability?
Regular maintenance includes torque checks on bolts, inspection of gaskets, and visual assessments for signs of wear or corrosion. Proper tightening of bolts is essential to maintain a tight seal.
- Can flanges and fittings be customized for unique projects?
Yes, flanges and fittings can be customized in terms of material, size, and design to meet the unique requirements of your project, allowing for tailored solutions.
- How can I ensure that flanges and fittings comply with industry standards?
Purchase flanges and fittings from reputable suppliers who adhere to industry standards such as ANSI/ASME, DIN, JIS, or ISO. Verify that the fittings have the appropriate certification.
- Are there alternatives to flanges and fittings for specific applications?
Yes, for certain applications, alternatives like compression fittings, push-to-connect fittings, or welding may be more suitable. The choice depends on factors like system design and operational needs.
For visual reference, you can find images of flanges and fittings on Texas Flange or Wikipedia
In conclusion, flanges and fittings may not grab headlines, but they are essential for the smooth operation of fluid systems in various industries. Their diversity, standards, and adaptability make them indispensable components in plumbing and piping systems worldwide.